Inguinal Hernia
Inguinal Hernia (Harnia) is a common problem seen in children, both male and female. Its reported incidence in children is 1 in every 10 live births, which means that if 100 children are born at any time, approximately 10 of them must be having an inguinal hernia.
This condition is more common in boys than girls. Also, it is more common among Premature (those born before the expected date of delivery).
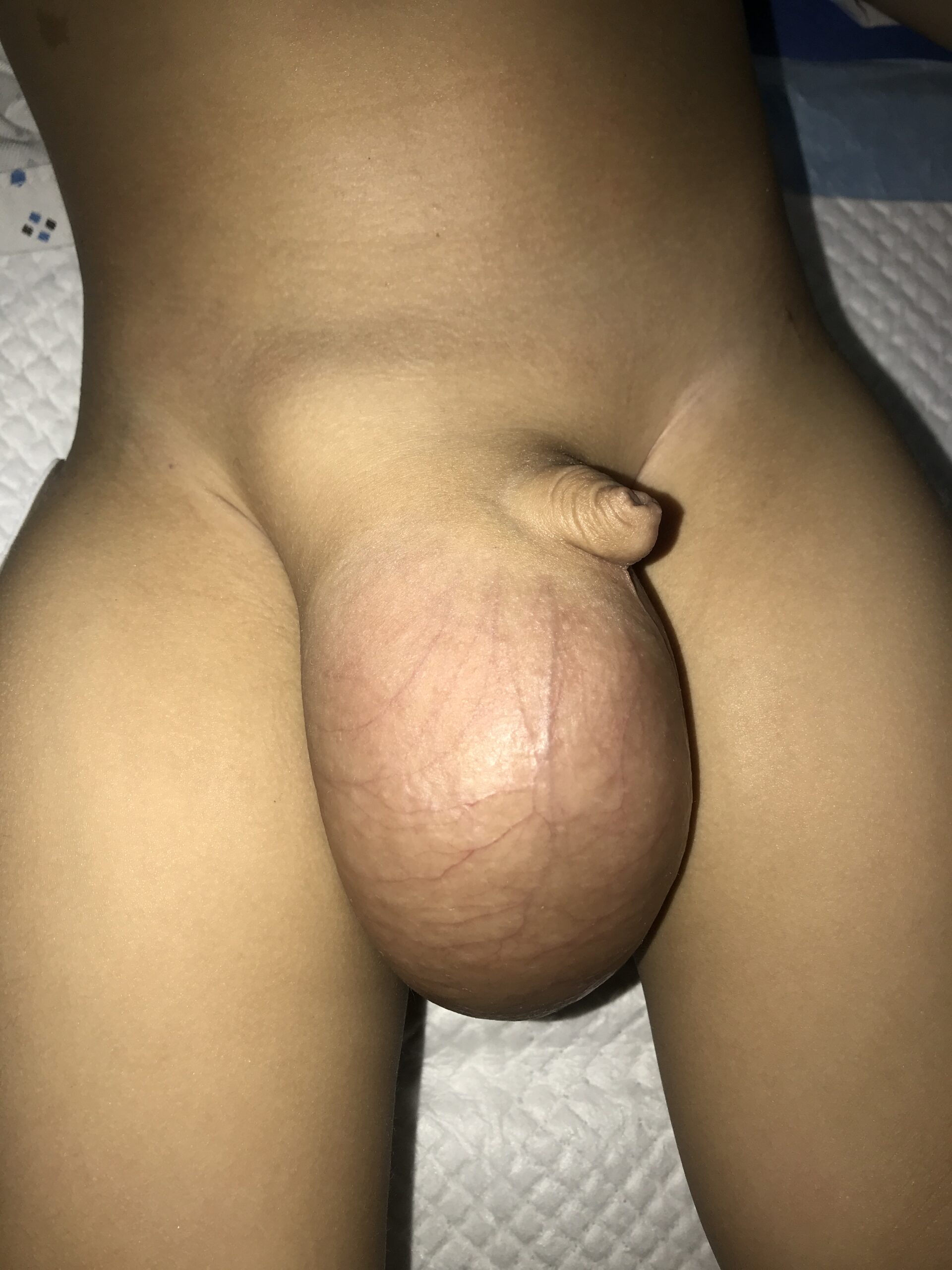
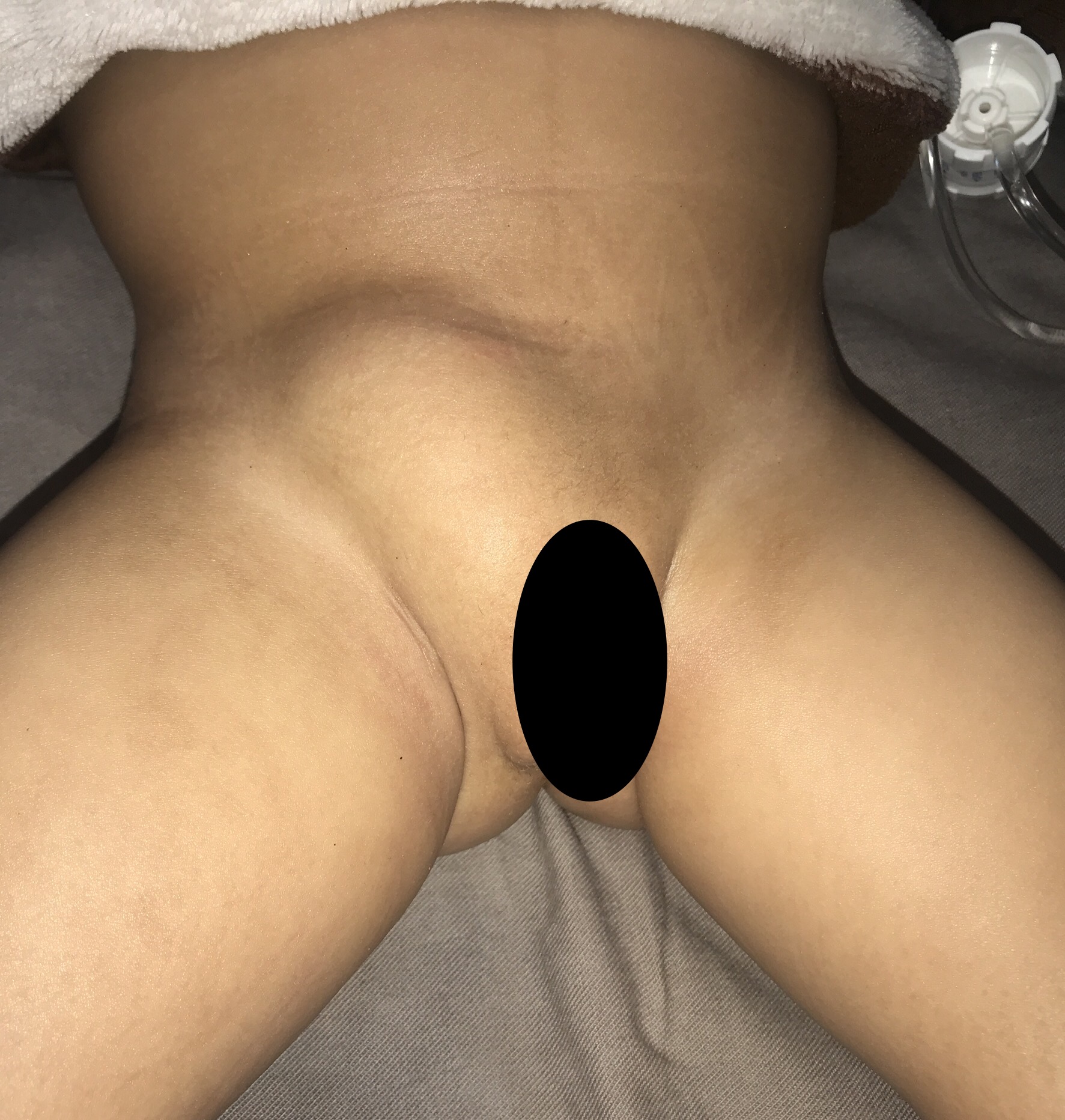

Children present with a bulge in their inguinal region, which increases in size during straining, weeping, and exercise times. Among males, this bulge comes to the scrotum and towards the testis. Among females, this bulge comes towards the vagina and labia.
It most commonly occurs on the right side and less commonly on the left side. In some children, an inguinal hernia occurs on both sides also (20%).
Diagnosis:
We usually diagnose it on the basis of history and examination. After the diagnosis, we will get some tests. These include Complete blood count, Hepatitis B, and C screening, and Ultrasound of this region.
Treatment:
The only treatment available for Inguinal Hernia (Harnia) in children is surgery. Some quacks claim that they can treat it with medications. However, technically it is not possible, and the only treatment is surgery.
Whenever a child with this condition presents, it is better to go for his surgery as soon as possible. If not timely treated, there are higher chances of incarceration, obstruction, and gangrene in these children. It there is obstruction, then there is an emergency need for surgery. In this case, it is a major surgery.
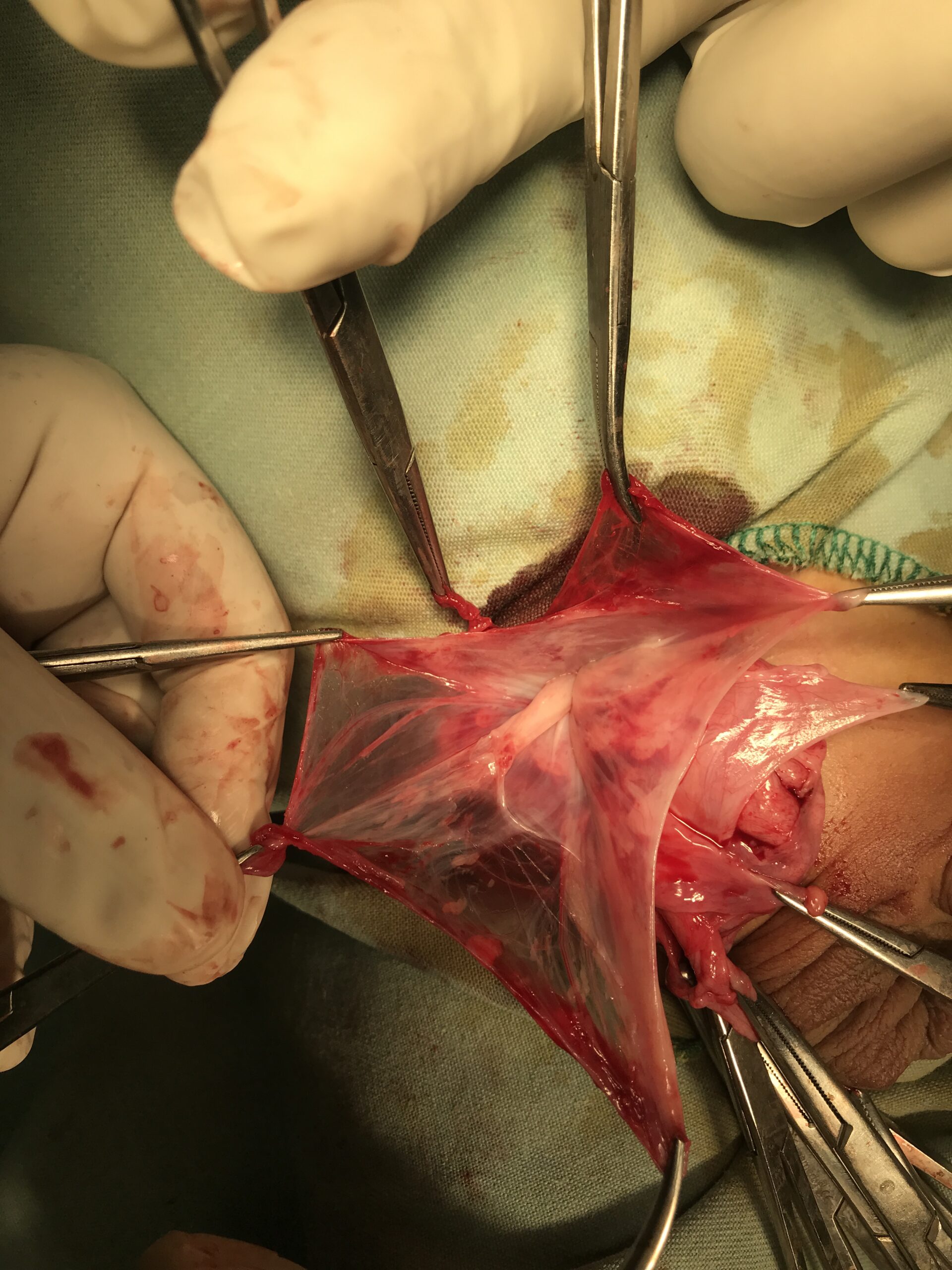
We can perform this surgery both Laparoscopically as well as open surgery. However, most surgeons globally like to do it as an open procedure because Laparoscopy does not have any added advantage in this condition. Sometimes, it is associated with Undescended testis, then both conditions are dealt in the same surgery.
Also Read:
کیا بچوں میں بھی ہرنیا ہوتا ہے؟
Five tips regarding post-operative care
Related Links:
Some FAQ's About Inguinal Hernia
A child with an inguinal hernia may experience a bulge in the groin area when they are crying, coughing, or straining to have a bowel movement. The bulge often disappears during quiet periods or while resting. Inguinal hernias usually do not cause pain. However, if it is obstructed, it will cause pain.
Inguinal hernia surgery is always needed and you can count on your child having the procedure under general anesthesia. What does this mean? It means that he will be sound asleep during his surgery!
Approximately 3-5% of healthy, full-term babies are born with an inguinal hernia. The incidence is substantially increased in premature infants: up to 30%. If left untreated, it can cause serious problems.
An inguinal hernia is not always dangerous, but it doesn’t get better by itself and can lead to life-threatening complications. Your doctor will recommend surgery if an inguinal hernia becomes painful or enlarges. Inguinal hernia repair is a common surgical procedure. It is better to gets its surgery done as soon as possible.
In some cases, hernias can lead to serious complications if they are left untreated. It may lead to a damage to the intestine and sometimes the testis/ovaries.
This surgery generally takes about 30 minutes to 1 hour.